GOLDILOCS reformulates scene change detection as a 3D reconstruction problem over time, a key insight that unlocks state-of-the-art binary and multi-class change detection under zero-shot conditions on both real-world image pairs and sets.
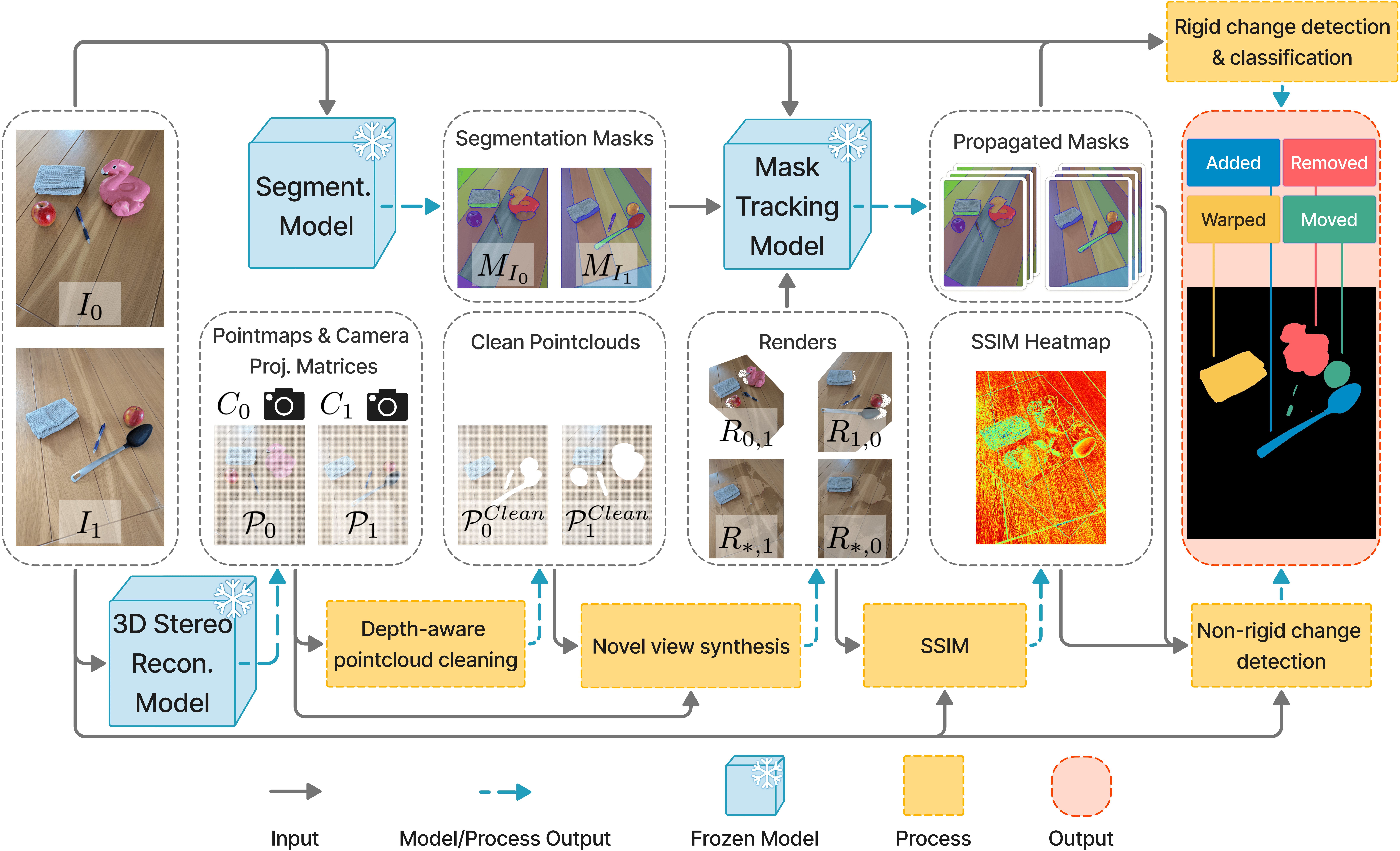
We propose GOLDILOCS: a novel zero-shot, pose-agnostic method for object-level semantic change detection in the wild. While supervised Scene Change Detection (SCD) methods achieve impressive results on curated datasets, these models do not generalize and performance drops on out-of-domain data. Recent Zero-Shot SCD methods introduced a more robust approach with foundational models as backbone, yet they neglect the 3D aspect of the task and remain constrained to the image-pair setting. Conversely, 3D-centric SCD methods based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) or NeRFs require multi-view inputs, but cannot operate on an image pair. Our key insight is that SCD can be reformulated as a 3D reconstruction problem over time, where geometric inconsistencies naturally indicate change. Although previous work considered viewpoint difference a challenge, we recognize the additional geometric information as an advantage. GOLDILOCS uses dense stereo reconstruction to estimate camera parameters and generate a pointmap of the commonalities between input images by filtering geometric inconsistencies. Ren- dering the canonical scene representation from multiple viewpoints yields reference images that exclude changed or occluded content. Rigid object changes are then detected through mask tracking, while nonrigid transformations are identified using SSIM heatmaps. We evaluate our method on a variety of datasets, covering both pairwise and multi-view cases in binary and multi-class settings, and demonstrate superior performance over prior work, including supervised methods.
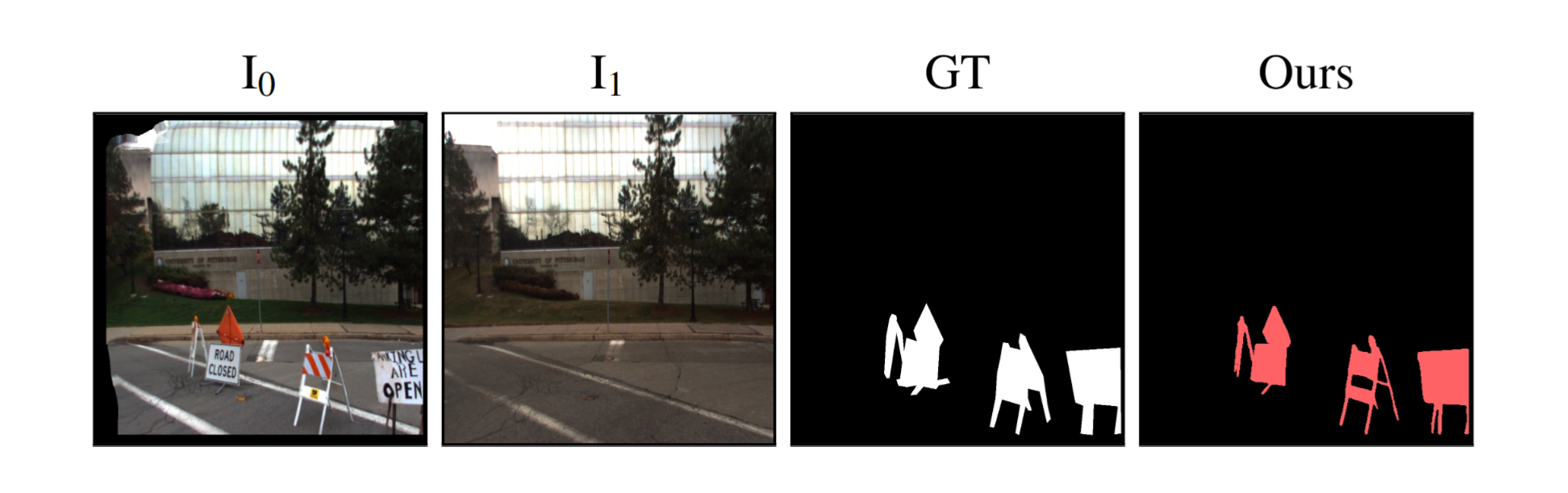
We evaluate our method across a diverse set of datasets including both real and simulated environments, indoor and outdoor scenes, and various types of change. Our results provide color-coded labels (Added, Removed, Moved, Replaced) even with binary GT and can exceed its accuracy, as annotations are often coarse or miss small changes.
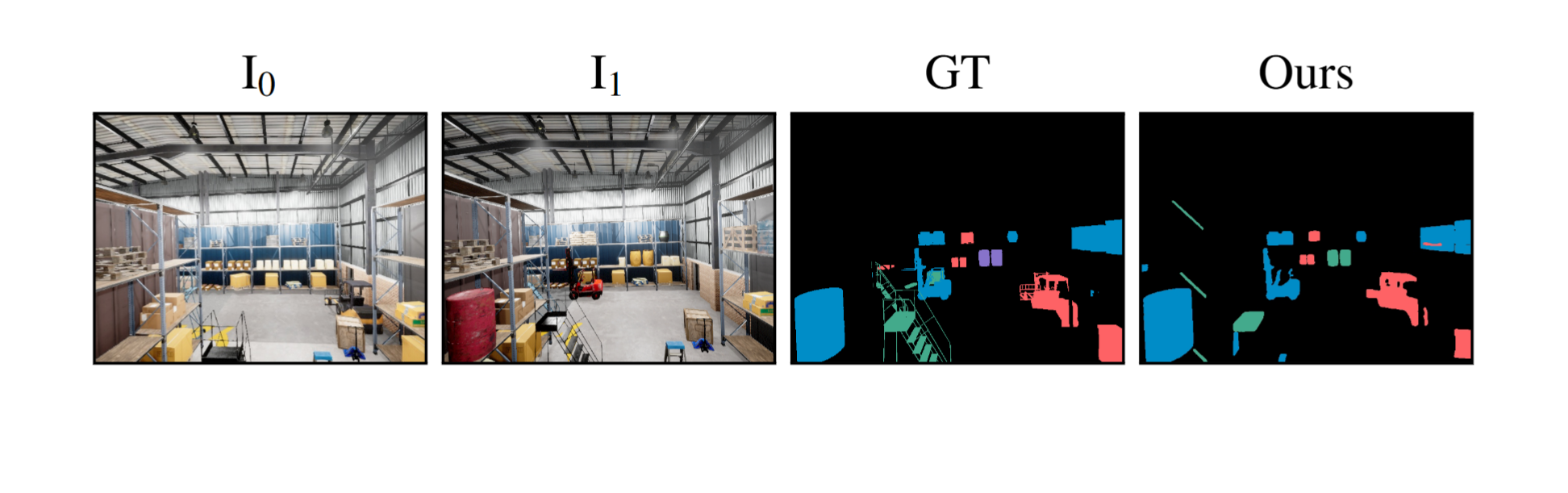
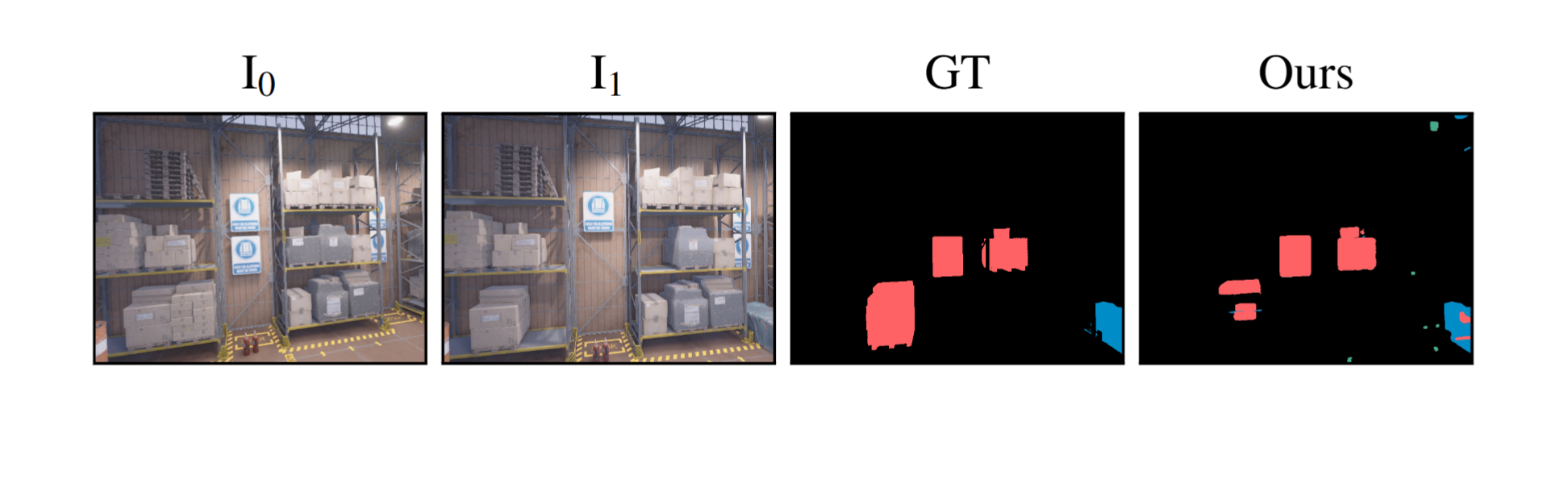
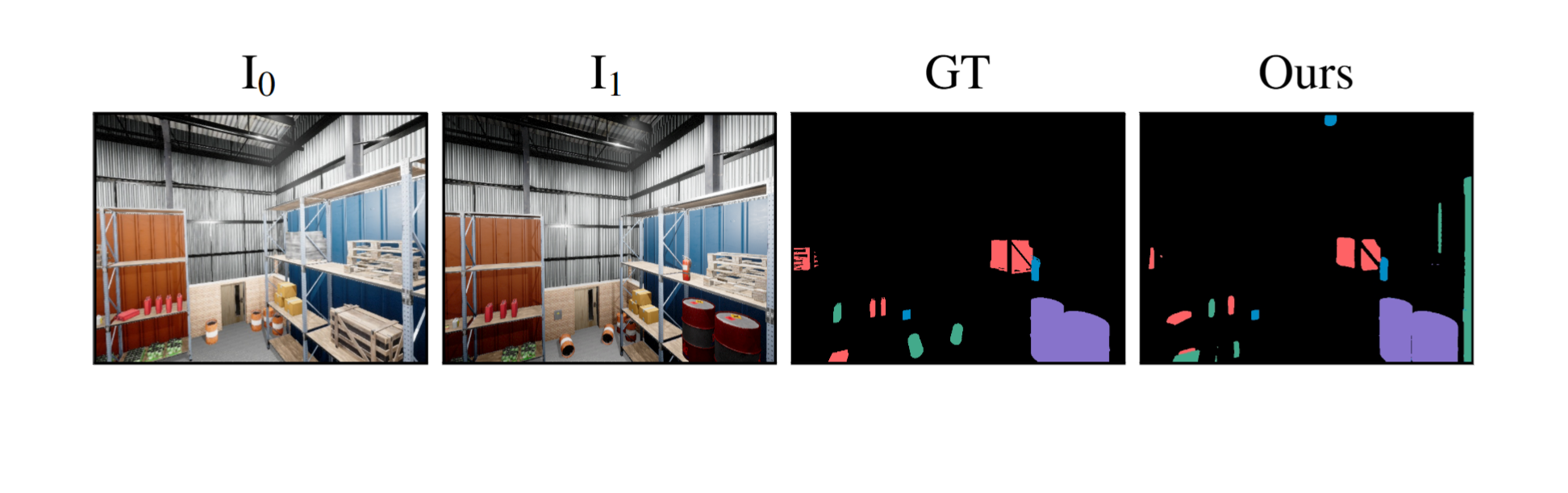
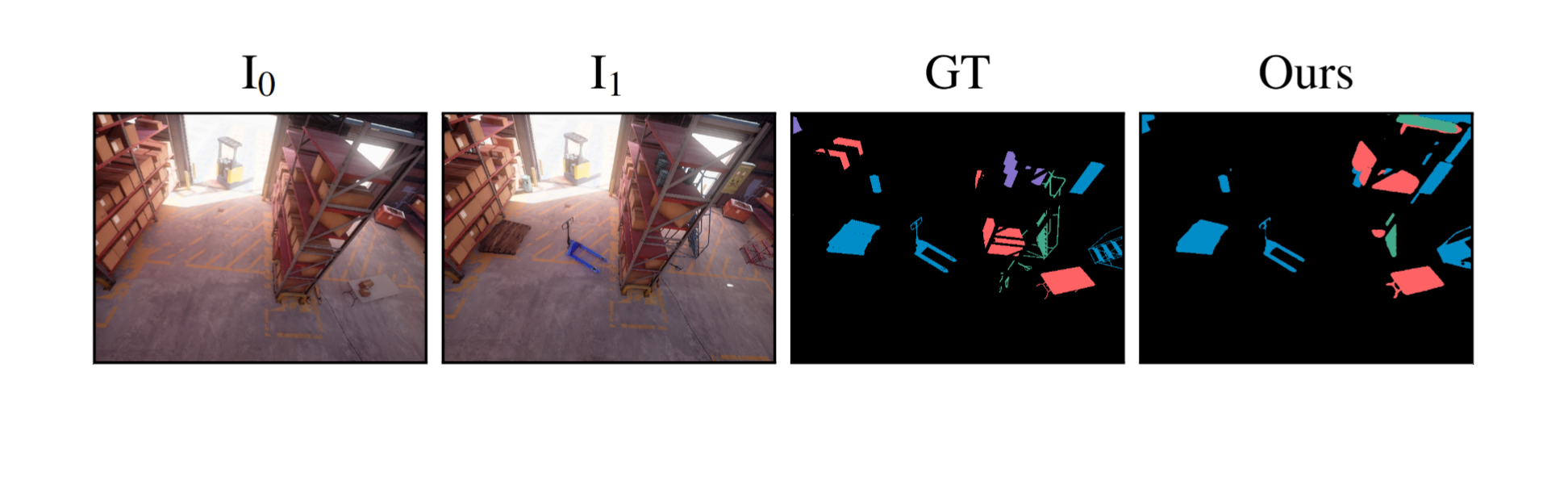

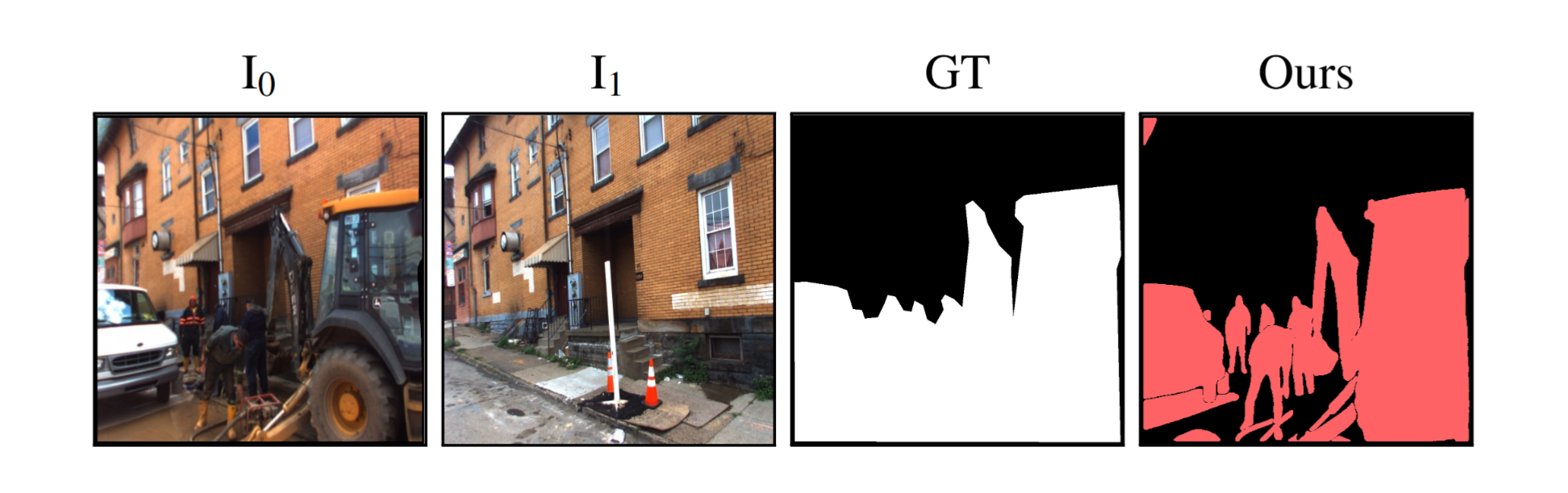


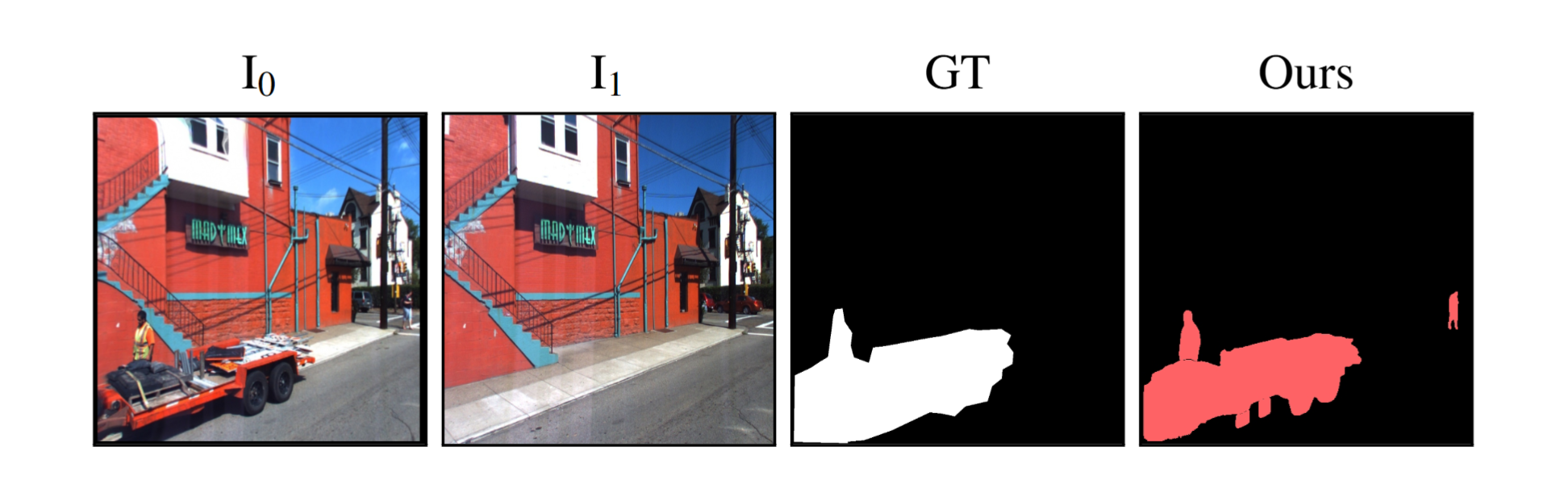
GOLDILOCS naturally extends from image pairs to multi-view scenarios, accommodating sets with multiple images at either or both timestamps. Compared to alternative approaches, GOLDILOCS is 10–100× faster than 3D Gaussian Splatting or NeRF-based methods, achieving superior benchmark performance without requiring auxiliary views or camera parameters.
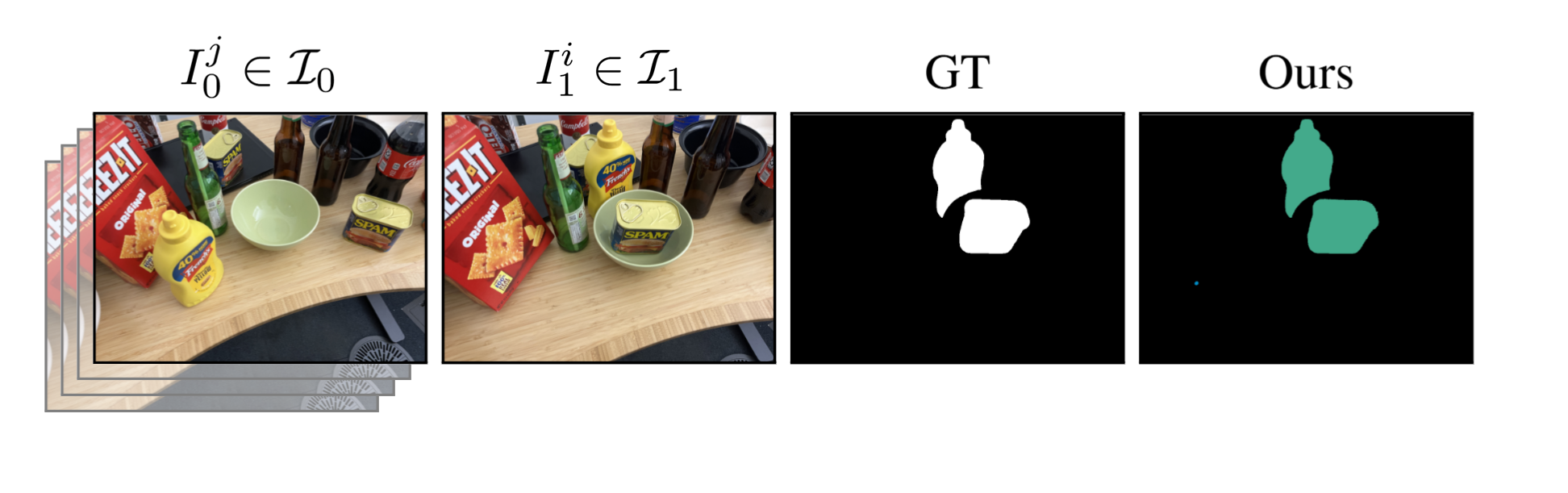
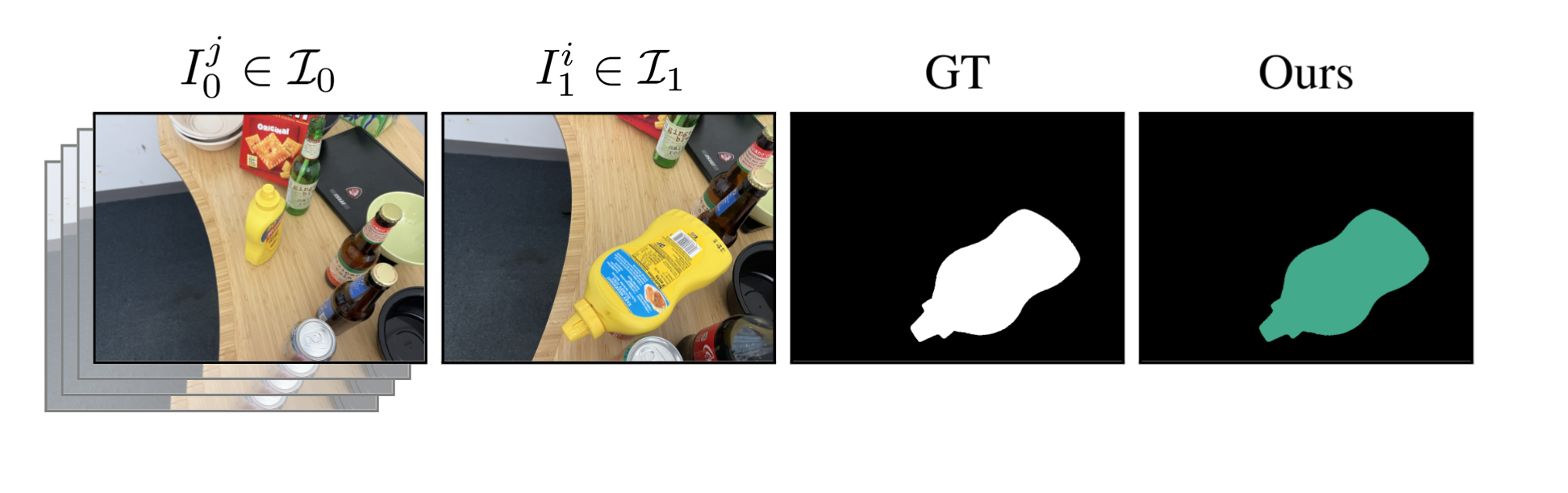

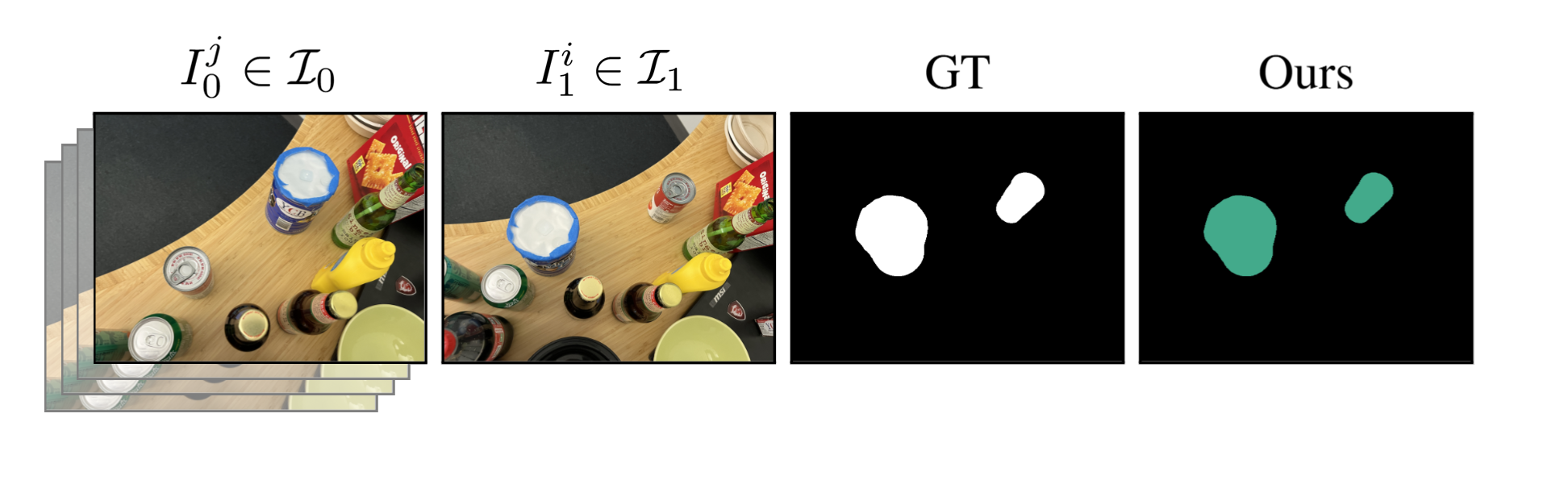


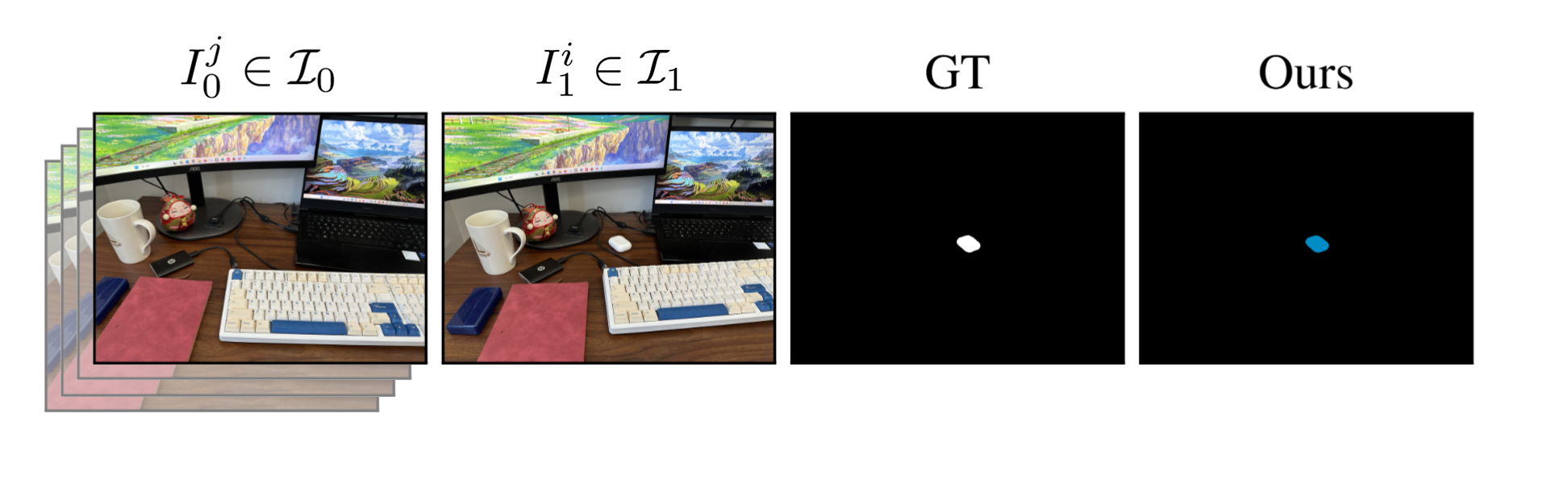

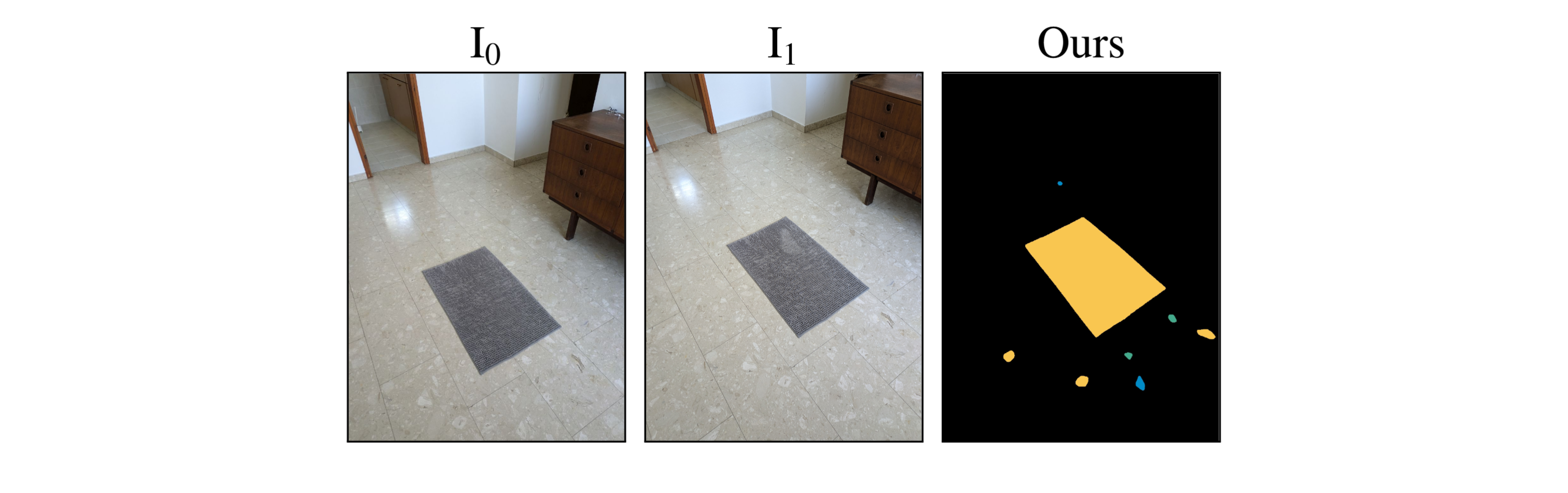
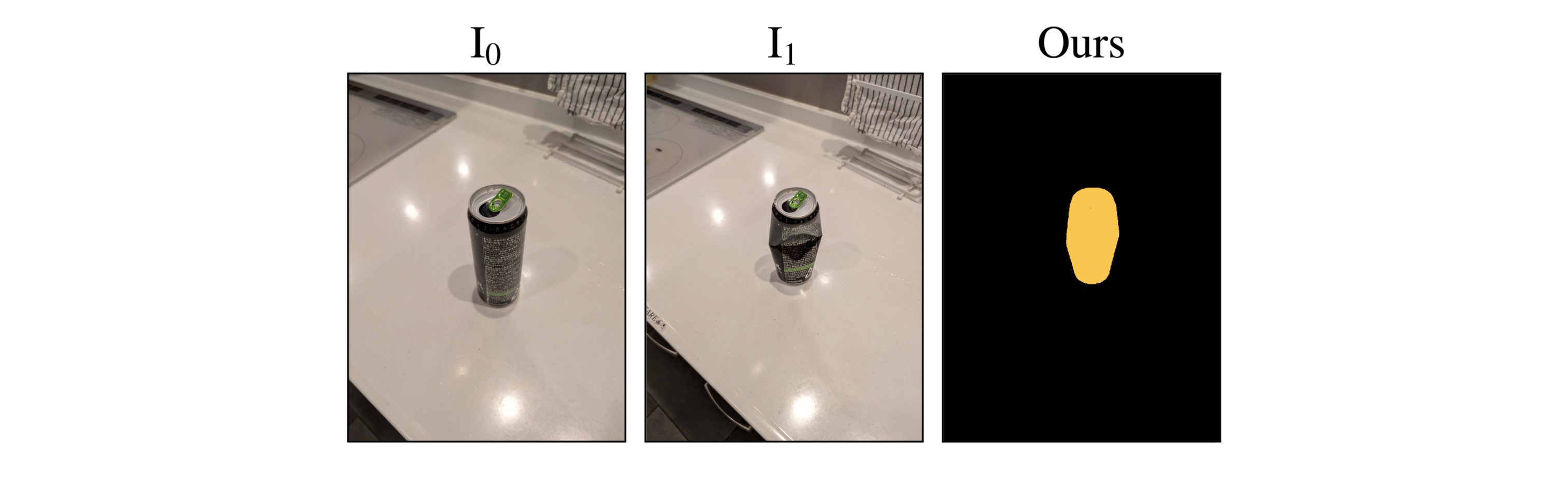
We evaluated our method on cases where objects have remained in place but undergone non-rigid transformations - such as creasing, denting, squashing and bending - a type of change we label as Warped. These results demonstrate GOLDILOC's ability to capture subtle shape deformations that do not involve displacement of the object itself. Notably, highly textured surfaces (e.g., the terrazzo tiles in the rug scene) represent a remaining challenge, occasionally triggering false positive detections.